H Cation Lewis Structure
Posted : admin On 3/19/2022Sp 2 hybridisation. The electronic configuration of carbon (Z = 6) in the excited state is. In this type of hybridization one- s and two P-orbitals of the valence shell of carbon atom take part in hybridization go give three new sp 2 hybrid orbitals. These sp 2 hybrid orbitals lie in a plane and are directed towards the corners of an equilateral triangle with a carbon atom in the centre. Electron dot diagrams for ions are the same as for atoms, except that some electrons have been removed for cations, while some electrons have been added for anions. Thus in comparing the electron configurations and electron dot diagrams for the Na atom and the Na + ion, we note that the Na atom has a single valence electron in its Lewis diagram. Draw the Lewis structure for the polyatomic hydronium (H,o') cation. Be sure to include all resonance structures that satisfy the octet rule.
A hydrogen ion is created when a hydrogen atom loses or gains an electron. A positively Removal of the electron gives a cation (left), whereas addition of an electron gives an anion (right).
Ionic Compounds: Lewis Dot Structures
The hydrogen anion, with its loosely held. Draw a Lewis electron dot diagram for an atom or a monatomic ion.
have been removed for cations, while some electrons have been added for anions. The Lewis symbol, more commonly 'Lewis structure,' of H+ is just H The hydrogen has been stripped of its only electron to form the positive ion.
Lewis Structures (electron dot diagrams) Lewis Structures of Atoms The gained or lost 1e lost Example Lewis Structure (electron dot diagram) H+ 2+ 3+ 2e lost Li2O Each lithium atom loses one electron to form 2 cations Li+ (2 electrons in. Learning Check: Lewis Dot Structure.
•Now it's your turn to try and draw some Charges (Cations). Group 1A.
Group 2A. Group 3A. H+. Mg2+.
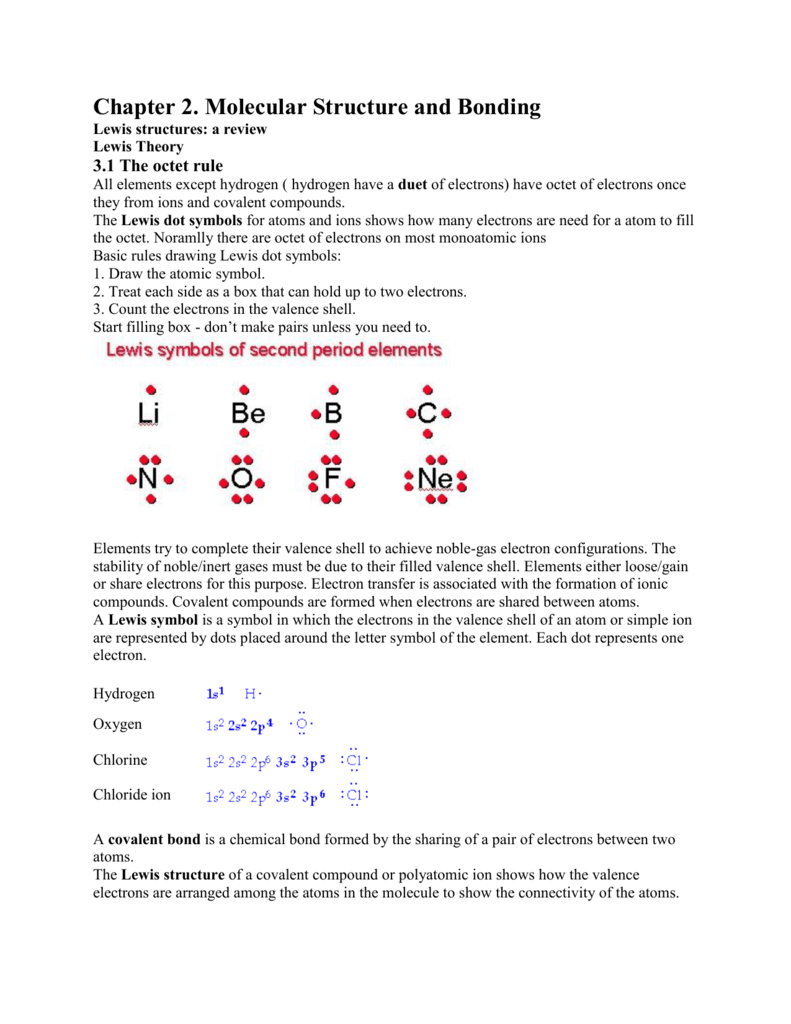
Valence electronic structures can be visualized by drawing Lewis symbols (for atoms and monatomic ions) and Lewis structures (for molecules and polyatomic ions). Lone pairs, unpaired electrons, and single, double, or triple bonds are used to indicate where the valence electrons are located around each atom in a Lewis structure. Zundel cation A hydrogen atom is made up of a nucleus with charge +1, and a single electron. Therefore, the only positively charged ion possible has charge +1. It is noted H +.
Al3+. Li+.
Ca2+.Electron Distributions Into Shells for the First Three Periods. A chemical element is identified by the number of protons in its nucleus, and it must collect an equal number of electrons if .
Hydron is the general name for the hydrogen nucleus, to be used without regard to the hydrogen nuclear mass (either for hydrogen in its natural abundance or where it is not desired to distinguish between the isotopes). It is a member of atomic nucleus, a monoatomic hydrogen, a monoatomic monocation and a monovalent inorganic cation.
Valence Electrons and Lewis Electron Dots of Atoms and Ions G.N. Lewis, at the University of California at Berkeley devised a simple way to understand the nature of the chemical bond in both ionic and molecular compounds. The Lewis Structure (electron dot diagram) of each ion is used to construct the Lewis Structure (electron dot diagram) for the ionic compound.

The Lewis structure of a positive ion (cation) is positioned adjacent to the Lewis structure of a negative ion (anion). OR H+.
OR Li+. OR Be2+ OR B3+ OR C4+ Lewis Structures for Ionic Compounds. The overall charge on the compound must equal zero, that is, the number of electrons lost by one atom must equal the number of electrons gained by the other atom.
Phosphate Ion Lewis Structure
The Lewis Structure (electron dot diagram) of each ion is used to construct the Lewis Structure (electron.what is the lewis symbol of H+? Yahoo AnswersLewis structure - Wikipedia